Amplitude modulation: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==What is AM?== |
==What is AM?== |
||
Amplitude Modulation is the done by modulating the Amplitude of an sinoid Carrier signal |
Amplitude Modulation is the done by modulating the Amplitude of an sinoid Carrier signal using the incoming signal. |
||
The Carrier Signal has usually a higher [[Frequency]] than the modulating signal. |
|||
The Carrier signal is a sinusoid with a fixed [[Frequency]] at least twice as high as the highest frequency occuring in the spectrum of the incoming signal. Usually a much higher frequency is choosen. |
|||
Amplitude Modulation schemes have been widely used in Analog Radio. |
|||
==Mathematical Setting== |
|||
The output signal is the simple product of incoming signal and Carrier Signal. |
|||
==An Example== |
==An Example== |
||
{| |
{| |
||
|[[Image:AM_picture1.jpg|Carrier Signal in time domain]] |
|[[Image:AM_picture1.jpg|Carrier Signal in time domain]] |
||
| Line 14: | Line 26: | ||
|} |
|} |
||
== |
==Special Kinds of AM== |
||
*DSSC, double side band supressed carrier |
*DSSC, double side band supressed carrier |
||
*SSB, single side band |
*SSB, single side band |
||
*residual sideband modulation (modulation used for analog TV applications) |
*residual sideband modulation (modulation used for analog TV applications) |
||
*[[Quadrature_Amplitude_Modulation|QAM]] |
*[[Quadrature_Amplitude_Modulation|QAM]] |
||
---- |
---- |
||
Revision as of 13:59, 27 September 2004
What is AM?
Amplitude Modulation is the done by modulating the Amplitude of an sinoid Carrier signal using the incoming signal.
The Carrier signal is a sinusoid with a fixed Frequency at least twice as high as the highest frequency occuring in the spectrum of the incoming signal. Usually a much higher frequency is choosen.
Amplitude Modulation schemes have been widely used in Analog Radio.
Mathematical Setting
The output signal is the simple product of incoming signal and Carrier Signal.
An Example
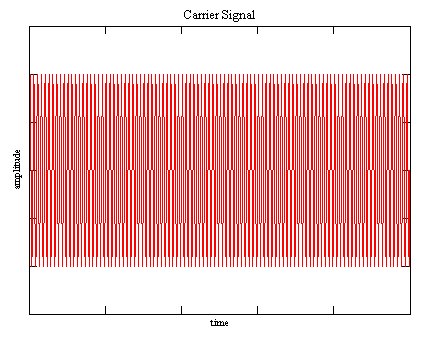
|
Carrier Signal in frequency domain (to be added) |
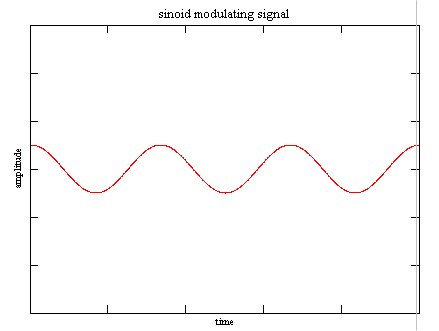
|
Modulating Signal in frequency domain (to be added) |
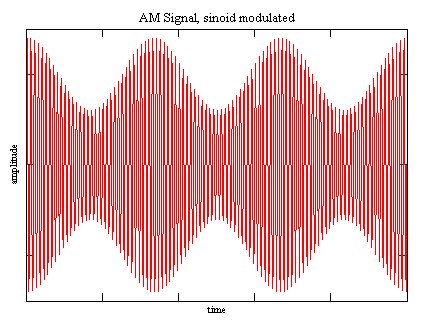
|
AM Signal in frequency domain (to be added) |
Special Kinds of AM
- DSSC, double side band supressed carrier
- SSB, single side band
- residual sideband modulation (modulation used for analog TV applications)
- QAM
Links: