Quadrature amplitude modulation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Voidxor moved page Quadrature Amplitude Modulation to Quadrature amplitude modulation: Not a proper noun) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
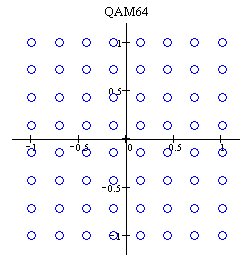
'''Quadrature amplitude modulation''' ('''QAM''') is a [[modulation scheme]] where both phase and amplitude are modulated in order to encode each symbol. The attached number specifies how many different states can get encoded (e.g. QAM-64 encodes 64 states in the [[Phase Diagram]], QAM-256 encodes 256 states). The following pictures give you an idea what happens: |
|||
The following pictures give you an idea what happens. |
|||
{| |
{| |
||
|[[ |
| [[File:QAM64.jpg|Principle of QAM64]] |
||
|[[ |
| [[File:QAM256.jpg|Principle of QAM256]] |
||
|} |
|} |
||
| ⚫ | The more states are encoded for a given allowed signal [[ |
||
| ⚫ | The more states are encoded for a given allowed signal [[bandwidth]] the more susceptible the signal is to noise. On the other hand, the more states are possible the more bandwidth is in theory possible. But only if the signal quality is good enough to decide between the different states because amplitude noise and phase noise will disturb the signal. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
U.S. networks also seem to use [[8VSB]] Modulation then and when. |
|||
US broadcasters use [[8VSB]] modulation. |
|||
[[Category:Technology]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 05:48, 27 December 2016
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is a modulation scheme where both phase and amplitude are modulated in order to encode each symbol. The attached number specifies how many different states can get encoded (e.g. QAM-64 encodes 64 states in the Phase Diagram, QAM-256 encodes 256 states). The following pictures give you an idea what happens:
|

|
The more states are encoded for a given allowed signal bandwidth the more susceptible the signal is to noise. On the other hand, the more states are possible the more bandwidth is in theory possible. But only if the signal quality is good enough to decide between the different states because amplitude noise and phase noise will disturb the signal.
Quadrature amplitude modulation is usually used for DVB-C and DVB-T, typically QAM-16, QAM-64 or (in Finnish cable networks) QAM-128 are used.
US broadcasters use 8VSB modulation.