GStreamer: Difference between revisions
(Another refactoring and expansion, part 1) |
(Another refactoring and expansion, part 2) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Getting Started with GStreamer == |
== Getting Started with GStreamer == |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | GStreamer, its most common plugins |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | GStreamer, its most common plugins and tools are available through your distribution's package manager. But <code>entrans</code> and some of the plugins used in the examples below are not. You can find their sources bundled by the [http://sourceforge.net/projects/gentrans/files/gst-entrans/ GEntrans project] at sourceforge. Google may help you to find precompiled packages for your distro. |
||
Two series of GStreamer are available - ''0.10'' and ''1.0''. Most Linux distributions include both, but this page discusses the older ''0.10'' series because I was unable to get the ''1.0'' series to work with my TV card. Converting the commands below to work with ''1.0'' is mostly just search-and-replace work (e.g. changing instances of <code>ff</code> to <code>av</code> because of the switch from <code>ffmpeg</code> to <code>libavcodec</code>). See [http://gstreamer.freedesktop.org/data/doc/gstreamer/head/manual/html/chapter-porting-1.0.html the porting guide] for more. |
Two series of GStreamer are available - ''0.10'' and ''1.0''. Most Linux distributions include both, but this page discusses the older ''0.10'' series because I was unable to get the ''1.0'' series to work with my TV card. Converting the commands below to work with ''1.0'' is mostly just search-and-replace work (e.g. changing instances of <code>ff</code> to <code>av</code> because of the switch from <code>ffmpeg</code> to <code>libavcodec</code>). See [http://gstreamer.freedesktop.org/data/doc/gstreamer/head/manual/html/chapter-porting-1.0.html the porting guide] for more. |
||
| Line 43: | Line 47: | ||
No two use cases for encoding are quite alike. Is your processor fast enough to encode high quality video? Do you want to play your video in DVD players, or is it enough that it works in your version of [http://www.videolan.org/vlc/index.en_GB.html VLC]? Which obscure quirks does your system have? |
No two use cases for encoding are quite alike. Is your processor fast enough to encode high quality video? Do you want to play your video in DVD players, or is it enough that it works in your version of [http://www.videolan.org/vlc/index.en_GB.html VLC]? Which obscure quirks does your system have? |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
=== Why prefer GStreamer? === |
=== Why prefer GStreamer? === |
||
GStreamer is better than most tools at synchronising audio with video in disturbed sources such as VHS tapes. If you specify your input is (say) 25 frames per second video and 48,000kHz audio, most tools will synchronise audio and video simply by writing 1 video frame, 1,920,000 audio frames, 1 video frame and so on. |
GStreamer is better than most tools at synchronising audio with video in disturbed sources such as VHS tapes. If you specify your input is (say) 25 frames per second video and 48,000kHz audio, most tools will synchronise audio and video simply by writing 1 video frame, 1,920,000 audio frames, 1 video frame and so on. There are at least three ways this can cause errors: |
||
* |
* '''initialisation timing''': audio and video desynchronised by a certain amount from the first frame, usually caused by audio and video devices taking different amounts of time to initialise. For example, the first audio frame might be delivered to GStreamer 0.01 seconds after it was requested, but the first video frame might not be delivered until 0.7 seconds after it was requested, causing all video to be 0.6 seconds behind the audio |
||
** <code>mencoder</code>'s ''-delay'' option solves this by delaying the audio |
** <code>mencoder</code>'s ''-delay'' option solves this by delaying the audio |
||
* |
* '''failure to encode''': frames that desynchronise gradually over time, usually caused by audio and video shifting relative each other when frames are dropped. For example if your CPU is not fast enough and sometimes drops a video frame, after 25 dropped frames the video will be one second ahead of the audio |
||
** <code>mencoder</code>'s ''-harddup'' option solves this by duplicating other frames to fill in the gaps |
** <code>mencoder</code>'s ''-harddup'' option solves this by duplicating other frames to fill in the gaps |
||
* |
* '''source frame rate''': frames that aren't delivered at the advertised rate, usually caused by inaccurate clocks in the source hardware. For example, a low-cost webcam might deliver 25.01 video frames per second and 47,999kHz, causing your audio and video drifting apart by a second or so per hour |
||
** video tapes are especially problematic here - if you've ever seen a VCR struggle |
** video tapes are especially problematic here - if you've ever seen a VCR struggle during those few seconds between two recordings on a tape, you've seen them adjusting the tape speed to accurately track the source. Frame counts can vary enough during these periods to instantly desynchronise audio and video |
||
** <code>mencoder</code> has no solution for this problem |
** <code>mencoder</code> has no solution for this problem |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
# If you choose a container format that does not support timestamps (e.g. AVI), you must duplicate other frames to fill in the gaps by adding the <code>videorate</code> and <code>audiorate</code> plugins to the end of the relevant pipelines |
# If you choose a container format that does not support timestamps (e.g. AVI), you must duplicate other frames to fill in the gaps by adding the <code>videorate</code> and <code>audiorate</code> plugins to the end of the relevant pipelines |
||
To get accurate timestamps, specify the <code>do-timestamp=true</code> option for all your sources. This will ensure accurate timestamps are retrieved from the driver where possible. Sadly, many v4l2 drivers don't support timestamps - GStreamer will add timestamps for these drivers to stop audio and video drifting apart, but you will need to fix the |
To get accurate timestamps, specify the <code>do-timestamp=true</code> option for all your sources. This will ensure accurate timestamps are retrieved from the driver where possible. Sadly, many v4l2 drivers don't support timestamps - GStreamer will add timestamps for these drivers to stop audio and video drifting apart, but you will need to fix the initialisation timing yourself (discussed below). |
||
== Common caputuring issues and their solutions == |
== Common caputuring issues and their solutions == |
||
| Line 145: | Line 145: | ||
# That number is exactly one hundred times your framerate, so you should tell GStreamer e.g. <code>framerate=2502/100</code> |
# That number is exactly one hundred times your framerate, so you should tell GStreamer e.g. <code>framerate=2502/100</code> |
||
=== Fixing |
=== Fixing initialisation timing errors === |
||
If your hardware doesn't support timestamps, your encoded audio |
If your hardware doesn't support timestamps, your encoded audio and video might be desynchronised by a fixed amount throughout the video. This offset is based on too many factors to isolate (e.g. a new driver version might increase or decrease the value), so fixing this is a manual process that probably needs to be done every time you encode a file. |
||
'''Calculate your desired offset:''' |
'''Calculate your desired offset:''' |
||
| Line 154: | Line 154: | ||
# Open the video in your favourite video player |
# Open the video in your favourite video player |
||
# Adjust the A/V sync until it looks right to you - different players put this in different places, for example it's ''Tools > Track Synchronisation'' in VLC |
# Adjust the A/V sync until it looks right to you - different players put this in different places, for example it's ''Tools > Track Synchronisation'' in VLC |
||
# write down your desired |
# write down your desired offset |
||
If possible, look for (or create) [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clapperboard clapperboard]-like events - moments where an obvious visual element occurred at the same moment as an obvious audio moment. A hand clapping or a cup being placed on a table are good examples. |
If possible, look for (or create) [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clapperboard clapperboard]-like events - moments where an obvious visual element occurred at the same moment as an obvious audio moment. A hand clapping or a cup being placed on a table are good examples. |
||
| Line 190: | Line 190: | ||
Note: you can apply any <code>sox</code> filter this way, like normalising the volume or removing background noise. |
Note: you can apply any <code>sox</code> filter this way, like normalising the volume or removing background noise. |
||
==== A specific solution for measuring your |
==== A specific solution for measuring your offset ==== |
||
Measuring your |
Measuring your offset will probably be the most unique part of your recording solution. Here is one solution you could use when digitising old VHS tapes: |
||
# Connect a camcorder to your VCR |
# Connect a camcorder to your VCR |
||
| Line 205: | Line 205: | ||
You'll probably need to change every step of the above to match your situation, but hopefully it will provide some inspiration. |
You'll probably need to change every step of the above to match your situation, but hopefully it will provide some inspiration. |
||
=== Avoiding pitfalls |
=== Avoiding pitfalls with video noise === |
||
If your video contains periods of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Noise_(video) video noise] (snow), you may need to deal with some extra issues: |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | * The ''stamp'' plugin gets confused by periods of snow |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | * The ''stamp'' plugin gets confused by periods of snow, causing it to generate faulty timestamps and framedropping. ''stamp'' will recover normal behaviour when the break is over, but will probably leave the buffer full of weirdly-stamped frames. ''stamp'' only drops one weirdly-stamped frame each sync-interval, so it can take several minutes until everything works fine again. To solve this problem, set ''leaky=2'' on each ''queue'' element to allow dropping old frames |
||
* Periods of noise (snow, bad signal etc.) are hard to encode. Variable bitrate encoders will often drive up the bitrate during the noise then down afterwards to maintain the average bitrate. To minimise these issues, specify a minimum and maximum bitrate in your encoder |
* Periods of noise (snow, bad signal etc.) are hard to encode. Variable bitrate encoders will often drive up the bitrate during the noise then down afterwards to maintain the average bitrate. To minimise these issues, specify a minimum and maximum bitrate in your encoder |
||
| Line 360: | Line 362: | ||
Note: as of August 2015, this script is still being fine-tuned. Come back in a month or two to see the final version. |
Note: as of August 2015, this script is still being fine-tuned. Come back in a month or two to see the final version. |
||
<nowiki> |
<nowiki>#!/bin/bash |
||
#!/bin/bash |
|||
# |
# |
||
# GStreamer lets you build a pipeline (a DAG of elements) to process audio and video. |
# GStreamer lets you build a pipeline (a DAG of elements) to process audio and video. |
||
| Line 507: | Line 508: | ||
echo_bold() { |
echo_bold() { |
||
echo -e "\e[1m$@\e[0m" |
echo -e "\e[1m$@\e[0m" |
||
} |
|||
show_progress() { |
|||
START_TIME="$( date +%s )" |
|||
PROGRESS_NEWLINE= |
|||
while read HEAD TAIL |
|||
do |
|||
if [ "$HEAD" = "progressreport0" ] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
NOW_TIME="$( date +%s )" |
|||
echo "$TAIL" | { |
|||
read TIME PROCESSED SLASH TOTAL REPLY |
|||
if [ "$PROCESSED" -eq 0 ] |
|||
then |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
else |
|||
echo -n $'\r'"$TAIL ETA:" $( date -d "$(( ( $(date +%s) - $START_TIME ) * ( $TOTAL - $PROCESSED ) / $PROCESSED )) seconds" ) |
|||
fi |
|||
} |
|||
PROGRESS_NEWLINE=$'\n' |
|||
else |
|||
echo "$PROGRESS_NEWLINE$HEAD $TAIL" |
|||
PROGRESS_NEWLINE= |
|||
fi |
|||
done |
|||
} |
} |
||
| Line 546: | Line 573: | ||
echo "Please delete $CONFIG_SCRIPT if you want to recreate it" |
echo "Please delete $CONFIG_SCRIPT if you want to recreate it" |
||
else |
else |
||
echo "$CONFIGURATION" > "$CONFIG_SCRIPT" |
|||
echo "Please edit $CONFIG_SCRIPT to match your system" |
|||
fi |
fi |
||
;; |
;; |
||
| Line 580: | Line 607: | ||
! wavenc \ |
! wavenc \ |
||
! filesink location="$FILE-temp.wav" \ |
! filesink location="$FILE-temp.wav" \ |
||
| show_progress |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
echo |
echo |
||
| Line 644: | Line 671: | ||
fi |
fi |
||
| ⚫ | |||
AUDIO_FILE="$FILE-temp.flac" |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
# Note: to make this script support a system where the video is ahead of the audio, |
|||
# change the `sox` commands below to `trim` the source audio instead of inserting silence before it |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
then |
then |
||
| ⚫ | |||
echo_bold "improving audio..." |
|||
then |
|||
exec 6< <( sox -V1 "$FILE-temp.wav" -t wav - trim "$NOISE_START" "$NOISE_DURATION" | sox -t wav - -n noiseprof - ) |
|||
NOISE_CMD="noisered /dev/fd/6 0.21" |
|||
noisered <( sox -V1 "$FILE-temp.wav" -t wav - trim "$NOISE_START" "$NOISE_DURATION" | sox -t wav - -n noiseprof - ) 0.21 |
|||
else |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
NOISE_CMD= |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
fi |
|||
echo_bold "improving audio..." |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
sox -S \ |
|||
X) |
|||
"$FILE-temp.wav" "$FILE-temp.flac" \ |
|||
# NO AUDIO DELAY |
|||
noisered <( sox -V1 "$FILE-temp.wav" -t wav - trim "$NOISE_START" "$NOISE_DURATION" | sox -t wav - -n noiseprof - ) 0.21 |
|||
exec 3< <( sox -V1 "$FILE-temp.wav" -t wav - $NOISE_CMD ) |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
;; |
|||
-) |
|||
echo_bold "improving audio..." |
|||
# NEGATIVE AUDIO DELAY - APPEND SILENCE |
|||
sox -S \ |
|||
exec 4< <( sox -V1 "$FILE-temp.wav" -t wav - trim 0.0 "$AUDIO_DELAY" ) |
|||
exec 5< <( sox -V1 -n -r "$AUDIO_BITRATE" -c 2 -t wav - trim 0.0 "${AUDIO_DELAY:1}" ) |
|||
exec 3< <( sox -V1 -t wav /dev/fd/4 -t wav /dev/fd/5 $NOISE_CMD ) |
|||
;; |
|||
*) |
|||
# POSITIVE AUDIO DELAY - PREPEND SILENCE |
|||
exec 4< <( sox -V1 -n -r "$AUDIO_BITRATE" -c 2 -t wav - trim 0.0 "$AUDIO_DELAY" ) |
|||
exec 5< <( sox -V1 "$FILE-temp.wav" -t wav - trim 0.0 -"$AUDIO_DELAY" ) |
|||
exec 3< <( sox -V1 -t wav /dev/fd/4 -t wav /dev/fd/5 $NOISE_CMD ) |
|||
;; |
|||
esac |
|||
else |
else |
||
exec 3< "$FILE-temp.wav" |
|||
fi |
fi |
||
| Line 674: | Line 706: | ||
echo_bold "building final file..." |
echo_bold "building final file..." |
||
nice -n +20 $GST_CMD -q \ |
nice -n +20 $GST_CMD -q \ |
||
uridecodebin uri="$URI-temp.mkv" |
uridecodebin uri="$URI-temp.mkv" ! progressreport ! ffenc_mpeg4 $GST_MPEG4_OPTS_PASS2 "multipass-cache-file=$FILE-temp.log" ! $GST_QUEUE ! mux.video_0 \ |
||
| ⚫ | |||
uridecodebin uri="file://$AUDIO_FILE" name=audio \ |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
video. ! progressreport ! deinterlace ! ffenc_mpeg4 $GST_MPEG4_OPTS_PASS2 "multipass-cache-file=$FILE-temp.log" ! $GST_QUEUE ! mux.video_0 \ |
|||
| show_progress |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
echo_bold "Saved to $FILE.avi" |
echo_bold "Saved to $FILE.avi" |
||
Revision as of 01:51, 6 August 2015
GStreamer is a toolkit for building audio- and video-processing pipelines. A pipeline might stream video from a file to a network, or add an echo to a recording, or (most interesting to us) capture the output of a Video4Linux device. Gstreamer is most often used to power graphical applications such as Totem, but this page will explain how to build an encoder using its command-line interface.
Getting Started with GStreamer
Use GStreamer if you want the best video quality possible with your hardware, and don't mind spending a weekend browsing the Internet for information.
Avoid GStreamer if you just want something quick-and-dirty, or can't stand programs with bad documentation and unhelpful error messages.
GStreamer, its most common plugins and tools are available through your distribution's package manager. But entrans and some of the plugins used in the examples below are not. You can find their sources bundled by the GEntrans project at sourceforge. Google may help you to find precompiled packages for your distro.
Two series of GStreamer are available - 0.10 and 1.0. Most Linux distributions include both, but this page discusses the older 0.10 series because I was unable to get the 1.0 series to work with my TV card. Converting the commands below to work with 1.0 is mostly just search-and-replace work (e.g. changing instances of ff to av because of the switch from ffmpeg to libavcodec). See the porting guide for more.
Using GStreamer with gst-launch
gst-launch is the standard command-line interface to GStreamer. Here's the simplest pipline you can build:
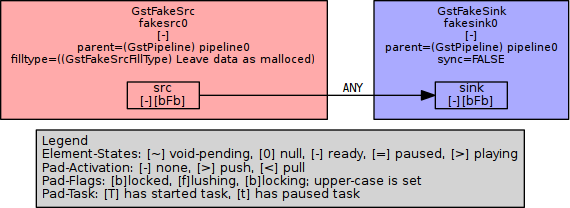
gst-launch-0.10 fakesrc ! fakesink
This connects a single (fake) source to a single (fake) sink using the 0.10 series of GStreamer:
To learn more about the source and sink elements, do:
gst-inspect-0.10 fakesrc gst-inspect-0.10 sink
If you have installed Graphviz, you can build a graph like the above yourself:
mkdir gst-visualisations GST_DEBUG_DUMP_DOT_DIR=gst-visualisations gst-launch-0.10 fakesrc ! fakesink dot -Tpng gst-visualisations/*-gst-launch.PLAYING_READY.dot > my-pipeline.png
To get graphs of the example pipelines below, prepend GST_DEBUG_DUMP_DOT_DIR=gst-visualisations to the gst-launch command. Run this command to generate a PNG version of GStreamer's most interesting stage:
dot -Tpng gst-visualisations/*-gst-launch.PLAYING_READY.dot > my-pipeline.png
Remember to empty the gst-visualisations directory between runs.
Using GStreamer with entrans
gst-launch is the main command-line interface to GStreamer, available by default. But entrans is a bit smarter:
- it provides partly-automatically composing of GStreamer pipelines
- it allows cutting of streams; e.g. to capture for a predefined duration. That ensures headers are written correctly, which is not always the case if you close
gst-launchby pressing Ctrl+C. To use this feature one has to insert a dam element after the first queue of each part of the pipeline
Using GStreamer for V4L TV capture
No two use cases for encoding are quite alike. Is your processor fast enough to encode high quality video? Do you want to play your video in DVD players, or is it enough that it works in your version of VLC? Which obscure quirks does your system have?
Why prefer GStreamer?
GStreamer is better than most tools at synchronising audio with video in disturbed sources such as VHS tapes. If you specify your input is (say) 25 frames per second video and 48,000kHz audio, most tools will synchronise audio and video simply by writing 1 video frame, 1,920,000 audio frames, 1 video frame and so on. There are at least three ways this can cause errors:
- initialisation timing: audio and video desynchronised by a certain amount from the first frame, usually caused by audio and video devices taking different amounts of time to initialise. For example, the first audio frame might be delivered to GStreamer 0.01 seconds after it was requested, but the first video frame might not be delivered until 0.7 seconds after it was requested, causing all video to be 0.6 seconds behind the audio
mencoder's -delay option solves this by delaying the audio
- failure to encode: frames that desynchronise gradually over time, usually caused by audio and video shifting relative each other when frames are dropped. For example if your CPU is not fast enough and sometimes drops a video frame, after 25 dropped frames the video will be one second ahead of the audio
mencoder's -harddup option solves this by duplicating other frames to fill in the gaps
- source frame rate: frames that aren't delivered at the advertised rate, usually caused by inaccurate clocks in the source hardware. For example, a low-cost webcam might deliver 25.01 video frames per second and 47,999kHz, causing your audio and video drifting apart by a second or so per hour
- video tapes are especially problematic here - if you've ever seen a VCR struggle during those few seconds between two recordings on a tape, you've seen them adjusting the tape speed to accurately track the source. Frame counts can vary enough during these periods to instantly desynchronise audio and video
mencoderhas no solution for this problem
GStreamer solves these problems by attaching a timestamp to each incoming frame based on the time GStreamer receives the frame. It can then mux the sources back together accurately using these timestamps, either by using a format that supports variable framerates or by duplicating frames to fill in the blanks:
- If you choose a container format that supports timestamps (e.g. Matroska), timestamps are automatically written to the file and used to vary the playback speed
- If you choose a container format that does not support timestamps (e.g. AVI), you must duplicate other frames to fill in the gaps by adding the
videorateandaudiorateplugins to the end of the relevant pipelines
To get accurate timestamps, specify the do-timestamp=true option for all your sources. This will ensure accurate timestamps are retrieved from the driver where possible. Sadly, many v4l2 drivers don't support timestamps - GStreamer will add timestamps for these drivers to stop audio and video drifting apart, but you will need to fix the initialisation timing yourself (discussed below).
Common caputuring issues and their solutions
Determining your video source
See all your video sources by doing:
ls /dev/video*
One of these is the card you want. Most people only have one, or can figure it out by disconnecting devices and rerunning the above command. Otherwise, check the capabilites of each device:
for VIDEO_DEVICE in /dev/video* ; do echo ; echo ; echo $VIDEO_DEVICE ; echo ; v4l2-ctl --device=$VIDEO_DEVICE --list-inputs ; done
Usually you will see e.g. a webcam with a single input and a TV card with multiple inputs. If you're still not sure which one is yours, try each one in turn:
v4l2-ctl --device=<device> --set-input=<whichever-input-you-want-to-use> gst-launch-0.10 v4l2src do-timestamp=true device=<device> ! autovideosink
(if your source is a VCR, remember to play a video so you know the right one when you see it)
If you like, you can store your device in an environment variable:
VIDEO_DEVICE=<device>
All further examples will use $VIDEO_DEVICE in place of an actual video device
Determining your audio source
See all of our audio sources by doing:
arecord -l
Again, it should be fairly obvious which of these is the right one. Get the device names by doing:
arecord -L | grep ^hw:
If you're not sure which one you want, try each in turn:
gst-launch-0.10 alsasrc do-timestamp=true device=hw:<device> ! autoaudiosink
Again, you should hear your tape playing when you get the right one. Note: always use an ALSA hw device, as they are closest to the hardware. Pulse audio devices and ALSA's plughw devices add extra layers that, while more convenient for most uses, only cause headaches for us.
Optionally set your device in an environment variable:
AUDIO_DEVICE=<device>
All further examples will use $AUDIO_DEVICE in place of an actual audio device
Reducing Jerkiness
If motion that should appear smooth instead stops and starts, try the following:
Check for muxer issues. Some muxers need big chunks of data, which can cause one stream to pause while it waits for the other to fill up. Change your pipeline to pipe your audio and video directly to their own filesinks - if the separate files don't judder, the muxer is the problem.
- If the muxer is at fault, add ! queue max-size-buffers=0 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0 immediately before each stream goes to the muxer
- queues have hard-coded maximum sizes - you can chain queues together if you need more buffering than one buffer can hold
Check your CPU load. When GStreamer uses 100% CPU, it may need to drop frames to keep up.
- If frames are dropped occasionally when CPU usage spikes to 100%, add a (larger) buffer to help smooth things out.
- this can be a source's internal buffer (e.g. v4l2src queue-size=16 or alsasrc buffer-time=2000000), or it can be an extra buffering step in your pipeline (! queue max-size-buffers=0 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0)
- If frames are dropped when other processes have high CPU load, consider using nice to make sure encoding gets CPU priority
- If frames are dropped regularly, use a different codec, change the parameters, lower the resolution, or otherwise choose a less resource-intensive solution
As a general rule, you should try increasing buffers first - if it doesn't work, it will just increase the pipeline's latency a bit. Be careful with nice, as it can slow down or even halt your computer.
Check for incorrect timestamps. If your video driver works by filling up an internal buffer then passing a cluster of frames without timestamps, GStreamer will think these should all have (nearly) the same timestamp. Make sure you have a videorate element in your pipeline, then add silent=false to it. If it reports many framedrops and framecopies even when the CPU load is low, the driver is probably at fault.
videorateon its own will actually make this problem worse by picking one frame and replacing all the others with it. Instead installentransand add its stamp element between v4l2src and queue (e.g. v4l2src do-timestamp=true ! stamp sync-margin=2 sync-interval=5 ! videorate ! queue)- stamp intelligently guesses timestamps if drivers don't support timestamping. Its sync- options drop or copy frames to get a nearly-constant framerate. Using
videorateas well does no harm and can solve some remaining problems
- stamp intelligently guesses timestamps if drivers don't support timestamping. Its sync- options drop or copy frames to get a nearly-constant framerate. Using
Measuring your video framerate
As mentioned above, some video cards produce slightly too many (or too few) frames per second. To check your system's actual frames per second, start your video source (e.g. a VCR or webcam) then run this command:
gst-launch-0.10 v4l2src ! fpsdisplaysink fps-update-interval=100000
- Let it run for 100 seconds to get a large enough sample. It should print some statistics in the bottom of the window - write down the number of frames dropped
- Let it run for another 100 seconds, then write down the new number of frames dropped
- Calculate
(second number) - (first number) - 1(e.g. 5007 - 2504 - 1 == 2502)- You need to subtract one because
fpsdisplaysinkdrops one frame every time it displays the counter
- You need to subtract one because
- That number is exactly one hundred times your framerate, so you should tell GStreamer e.g.
framerate=2502/100
Fixing initialisation timing errors
If your hardware doesn't support timestamps, your encoded audio and video might be desynchronised by a fixed amount throughout the video. This offset is based on too many factors to isolate (e.g. a new driver version might increase or decrease the value), so fixing this is a manual process that probably needs to be done every time you encode a file.
Calculate your desired offset:
- Record a video using one of the techniques below
- Open the video in your favourite video player
- Adjust the A/V sync until it looks right to you - different players put this in different places, for example it's Tools > Track Synchronisation in VLC
- write down your desired offset
If possible, look for (or create) clapperboard-like events - moments where an obvious visual element occurred at the same moment as an obvious audio moment. A hand clapping or a cup being placed on a table are good examples.
Extract your audio:
gst-launch-0.10 \ uridecodebin uri="file:///path/to/my.file" \ ! progressreport \ ! audioconvert \ ! audiorate \ ! wavenc \ ! filesink location="/path/to/my.file.wav"
If you have a clapperboard event, you might want to examine the extracted file in an audio editor like Audacity. You should be able to see the exact time of the clap sound in the audio stream, watch the video to isolate the exact frame, and use that information to calculate the precise audio delay.
Use sox to prepend some silence:
sox -S -t wav <( sox -V1 -n -r <bitrate> -c <audio-channels> -t wav - trim 0.0 <delay-in-seconds> ) "/path/to/my.file.wav" "/path/to/my.file.flac"
Mix the new audio and the old video into a new file:
gst-launch-0.10 \ uridecodebin uri="file:///path/to/my.file" \ ! video/your-video-settings \ ! mux. \ uridecodebin uri="file:///path/to/my.file.flac" \ ! audioconvert \ ! audiorate \ ! your_preferred_audio_encoder \ ! mux. \ avimux name=mux \ ! filesink location="/path/to/my.file.new"
Note: you can apply any sox filter this way, like normalising the volume or removing background noise.
A specific solution for measuring your offset
Measuring your offset will probably be the most unique part of your recording solution. Here is one solution you could use when digitising old VHS tapes:
- Connect a camcorder to your VCR
- Tune the VCR so it shows the camcorder output when it's not playing
- Start your GStreamer pipeline
- Clap your hands in front of the camcorder so you can later measure A/V synchronisation
- Press play on the VCR
- When the video has finished recording, split the audio and video tracks as described above
- Examine the audio with Audacity and identify the precise time of the clap sound
- Examine the video with avidemux and identify the frame of the clap image
You'll probably need to change every step of the above to match your situation, but hopefully it will provide some inspiration.
Avoiding pitfalls with video noise
If your video contains periods of video noise (snow), you may need to deal with some extra issues:
- Most video capturing devices send EndOfStream signals if the input signal quality drops too low, causing GStreamer to finish capturing. To prevent the device from sending EOS, set num-buffers=-1 on the v4l2src element.
- The stamp plugin gets confused by periods of snow, causing it to generate faulty timestamps and framedropping. stamp will recover normal behaviour when the break is over, but will probably leave the buffer full of weirdly-stamped frames. stamp only drops one weirdly-stamped frame each sync-interval, so it can take several minutes until everything works fine again. To solve this problem, set leaky=2 on each queue element to allow dropping old frames
- Periods of noise (snow, bad signal etc.) are hard to encode. Variable bitrate encoders will often drive up the bitrate during the noise then down afterwards to maintain the average bitrate. To minimise these issues, specify a minimum and maximum bitrate in your encoder
Sample pipelines
At some point, you will probably need to build your own GStreamer pipeline. Here are some examples to give you the basic idea:
Record raw video only
A simple pipeline that initialises one video source, sets the video format, muxes it into a file format, then saves it to a file:
gst-launch-0.10 \ v4l2src do-timestamp=true device=$VIDEO_DEVICE \ ! video/x-raw-yuv,width=640,height=480 \ ! avimux ! filesink location=test0.avi
tcprobe says this video-only file uses the I420 codec and gives the framerate as correct NTSC:
$ tcprobe -i test1.avi
[tcprobe] RIFF data, AVI video
[avilib] V: 29.970 fps, codec=I420, frames=315, width=640, height=480
[tcprobe] summary for test1.avi, (*) = not default, 0 = not detected
import frame size: -g 640x480 [720x576] (*)
frame rate: -f 29.970 [25.000] frc=4 (*)
no audio track: use "null" import module for audio
length: 315 frames, frame_time=33 msec, duration=0:00:10.510
The files will play in mplayer, using the codec [raw] RAW Uncompressed Video.
Record to ogg theora
Here is a more complex example that initialises two sources - one video and audio:
gst-launch-0.10 \ v4l2src do-timestamp=true device=$VIDEO_DEVICE \ ! video/x-raw-yuv,width=640,height=480,framerate=\(fraction\)30000/1001 \ ! ffmpegcolorspace \ ! theoraenc \ ! queue \ ! mux. \ alsasrc do-timestamp=true device=$AUDIO_DEVICE \ ! audio/x-raw-int,channels=2,rate=32000,depth=16 \ ! audioconvert \ ! vorbisenc \ ! mux. \ oggmux name=mux \ ! filesink location=test0.ogg
Each source is encoded and piped into a muxer that builds an ogg-formatted data stream. The stream is then saved to test0.ogg. Note the required workaround to get sound on a saa7134 card, which is set at 32000Hz (cf. bug). However, I was still unable to get sound output, though mplayer claimed there was sound -- the video is good quality:
VIDEO: [theo] 640x480 24bpp 29.970 fps 0.0 kbps ( 0.0 kbyte/s) Selected video codec: [theora] vfm: theora (Theora (free, reworked VP3)) AUDIO: 32000 Hz, 2 ch, s16le, 112.0 kbit/10.94% (ratio: 14000->128000) Selected audio codec: [ffvorbis] afm: ffmpeg (FFmpeg Vorbis decoder)
Record to mpeg4
This is similar to the above, but generates an AVI file with streams encoded using AVI-compatible encoders:
gst-launch-0.10 \ v4l2src do-timestamp=true device=$VIDEO_DEVICE \ ! video/x-raw-yuv,width=640,height=480,framerate=\(fraction\)30000/1001 \ ! ffmpegcolorspace \ ! ffenc_mpeg4 \ ! queue \ ! mux. \ alsasrc do-timestamp=true device=$AUDIO_DEVICE \ ! audio/x-raw-int,channels=2,rate=32000,depth=16 \ ! audioconvert \ ! lame \ ! mux. \ avimux name=mux \ ! filesink location=test0.avi
I get a file out of this that plays in mplayer, with blocky video and no sound. Avidemux cannot open the file.
GStreamer 1.0: record from a bad analog signal to MJPEG video and RAW mono audio
stamp is not available in GStreamer 1.0, cogcolorspace and ffmpegcolorspace have been replaced by videoconvert:
gst-launch-1.0 \ v4l2src do-timestamp=true device=$VIDEO_DEVICE do-timestamp=true \ ! 'video/x-raw,format=(string)YV12,width=(int)720,height=(int)576' \ ! videorate \ ! 'video/x-raw,format=(string)YV12,framerate=25/1' \ ! videoconvert \ ! 'video/x-raw,format=(string)YV12,width=(int)720,height=(int)576' ! jpegenc \ ! queue \ ! mux. \ alsasrc do-timestamp=true device=$AUDIO_DEVICE \ ! 'audio/x-raw,format=(string)S16LE,rate=(int)48000,channels=(int)2' \ ! audiorate \ ! audioresample \ ! 'audio/x-raw,rate=(int)44100' \ ! audioconvert \ ! 'audio/x-raw,channels=(int)1' \ ! queue \ ! mux. \ avimux name=mux ! filesink location=test.avi
As stated above, it is best to use both audiorate and videorate: you problably use the same chip to capture both audio stream and video stream so the audio part is subject to disturbance as well.
View pictures from a webcam
Here are some miscellaneous examples for viewing webcam video:
gst-launch-0.10 \ v4l2src do-timestamp=true use-fixed-fps=false \ ! video/x-raw-yuv,format=\(fourcc\)UYVY,width=320,height=240 \ ! ffmpegcolorspace \ ! autovideosink
gst-launch-0.10 \ v4lsrc do-timestamp=true autoprobe-fps=false device=$VIDEO_DEVICE \ ! "video/x-raw-yuv,format=(fourcc)I420,width=160,height=120,framerate=10" \ ! autovideosink
Entrans: Record to DVD-compliant MPEG2
entrans -s cut-time -c 0-180 -v -x '.*caps' --dam -- --raw \
v4l2src queue-size=16 do-timestamp=true device=$VIDEO_DEVICE norm=PAL-BG num-buffers=-1 ! stamp silent=false progress=0 sync-margin=2 sync-interval=5 ! \
queue silent=false leaky=2 max-size-buffers=0 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0 ! dam ! \
cogcolorspace ! videorate silent=false ! \
'video/x-raw-yuv,width=720,height=576,framerate=25/1,interlaced=true,aspect-ratio=4/3' ! \
queue silent=false leaky=2 max-size-buffers=0 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0 ! \
ffenc_mpeg2video rc-buffer-size=1500000 rc-max-rate=7000000 rc-min-rate=3500000 bitrate=4000000 max-key-interval=15 pass=pass1 ! \
queue silent=false leaky=2 max-size-buffers=0 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0 ! mux. \
pulsesrc buffer-time=2000000 do-timestamp=true ! \
queue silent=false leaky=2 max-size-buffers=0 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0 ! dam ! \
audioconvert ! audiorate silent=false ! \
audio/x-raw-int,rate=48000,channels=2,depth=16 ! \
queue silent=false max-size-buffers=0 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0 ! \
ffenc_mp2 bitrate=192000 ! \
queue silent=false leaky=2 max-size-buffers=0 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0 ! mux. \
ffmux_mpeg name=mux ! filesink location=my_recording.mpg
This captures 3 minutes (180 seconds, see first line of the command) to my_recording.mpg and even works for bad input signals.
- I wasn't able to figure out how to produce a mpeg with ac3-sound as neither ffmux_mpeg nor mpegpsmux support ac3 streams at the moment. mplex does but I wasn't able to get it working as one needs very big buffers to prevent the pipeline from stalling and at least my GStreamer build didn't allow for such big buffers.
- The limited buffer size on my system is again the reason why I had to add a third queue element to the middle of the audio as well as of the video part of the pipeline to prevent jerking.
- In many HOWTOs you find ffmpegcolorspace instead of cogcolorspace. You can even use this but cogcolorspace is much faster.
- It seems to be important that the video/x-raw-yuv,width=720,height=576,framerate=25/1,interlaced=true,aspect-ratio=4/3-statement is after videorate as videorate seems to drop the aspect-ratio-metadata otherwise resulting in files with aspect-ratio 1 in theis headers. Those files are probably played back warped and programs like dvdauthor complain.
Ready-made scripts
Although no two use cases are the same, it can be useful to see scripts used by other people. These can fill in blanks and provide inspiration for your own work.
Bash script to record video tapes with GStreamer (work-in-progress)
Note: as of August 2015, this script is still being fine-tuned. Come back in a month or two to see the final version.
#!/bin/bash
#
# GStreamer lets you build a pipeline (a DAG of elements) to process audio and video.
#
# At the time of writing, both the 0.1 and 1.0 series were installed by default.
# So far as I can tell, the 1.0 series has some kind of bug that breaks TV-recording utterly
# (possibly a bug in selecting the output formats from v4l2src)
# If the 1.0 series gets fixed, you should only need to change a few commands here and there
# (see http://gstreamer.freedesktop.org/data/doc/gstreamer/head/manual/html/chapter-porting-1.0.html)
#
# We also use `v4l2-ctl` from the v4l-utils package to set the input source,
# and `sox` (from the `sox` package) to edit the audio
#
# Approximate system requirements for maximum quality settings (smaller images and lower bitrates need less):
# * about 10GB free for every hour of recording (6-7GB for temporary files, 3-4GB for the output file)
# * 3GHz processor (preferably at least dual core, so other processes don't steal the encoder's CPU time)
# * about 2GB of memory for every hour of recording (the second encoding pass needs to see the whole file)
HELP_MESSAGE="Usage: $0 --init
$0 --record <directory>
$0 --kill <directory> <timeout>
$0 --process <directory>
$0 --clean <directory>
Record a video into a directory (one directory per video).
--init create an initial ~/.gstreamer-record-scriptrc
please edit this file before your first recording
--record create a first-pass recording in the specified directory
--kill stop the recording in the specified directory after a specific amount time
see \`man sleep\` for details about allowed time formats
--process build the final recording in the specified directory
make sure to edit \`.gstreamer-record-scriptrc\` in that directory first
--clean delete temporary files
"
CONFIGURATION='#
# CONFIGURATION FOR GSTREAMER RECORD SCRIPT
# For more information, see http://www.linuxtv.org/wiki/index.php/GStreamer
#
#
# VARIABLES YOU NEED TO EDIT
# Every system and every use case is slightly different.
# Here are the things you will probably need to change:
#
# Set these based on your hardware/location:
VIDEO_DEVICE=${VIDEO_DEVICE:-/dev/video0} # `ls /dev/video*` for a list
AUDIO_DEVICE=${AUDIO_DEVICE:-hw:CARD=SAA7134,DEV=0} # `arecord -L` for a list
NORM=${NORM:-PAL} # (search Wikipedia for the exact norm in your country)
VIDEO_KBITRATE="${VIDEO_KBITRATE:-8000}" # test for yourself, but 8000 seems to produce a high quality result (we use bitrate/1000 for readability and to help calculate the values below)
AUDIO_BITRATE="${AUDIO_BITRATE:-32000}" # only bitrate supported by SAA7134 drivers - do `arecord -D $AUDIO_DEVICE --dump-hw-params -d 1 /dev/null` to see what your device supports
VIDEO_INPUT="${VIDEO_INPUT:-1}" # composite input - `v4l2-ctl --device=$VIDEO_DEVICE --list-inputs` for a list
# PAL video is approximately 720x576 resolution. VHS tapes have about half the horizontal quality, but this post convinced me to encode at 720x576 anyway:
# http://forum.videohelp.com/threads/215570-Sensible-resolution-for-VHS-captures?p=1244415#post1244415
ASPECT_W="${ASPECT_W:-5}"
ASPECT_H="${ASPECT_H:-4}"
SIZE_MULTIPLIER="${SIZE_MULTIPLIER:-144}" # common multipliers include 144 (720x576 - PAL), 128 (640x480 - VGA) and 72 (360x288 - half PAL). Set this lower to reduce CPU usage
# GStreamer automatically keeps audio and video in sync, but most systems start recording audio shortly before video video.
# If your system has this problem...
#
# 1. run the first pass of AVI recording
# 2. watch the video in your favourite video player
# 3. adjust the audio delay until the video looks right
# 4. pass the relevant number to the second pass
# 5. if you plan to do several recordings in one session, you can set the following default value
#
# Note: you will have an opportunity to set the audio delay for a specific file later
AUDIO_DELAY="${AUDIO_DELAY:-0.3}"
# Some VCRs consistently run slightly fast or slow. If you suspect your VCR has this problem...
#
# Do a quick test:
# 1. Run this command: gst-launch-0.10 v4l2src ! fpsdisplaysink fps-update-interval=1000
# * this will measure your average frame rate every second. After a few seconds, it should say "drop rate 25.00"
# 2. Change "FRAMERATE" below to your actual frame rate (e.g. 2502/100 if your frame rate is 25.02 FPS)
#
# Or if you want to be precise:
# 1. Run this command: gst-launch-0.10 v4l2src ! fpsdisplaysink fps-update-interval=100000
# * this will measure your average frame rate every 100 seconds (you can try different intervals if you like)
# 2. wait 100 seconds, then record the number of frames dropped
# 3. wait another 100 seconds, then record the number of frames dropped again
# 4. calculate (result of step 4) - (result of step 3) - 1
# * e.g. 5007 - 2504 - 1 == 2502
# * you need to subtract one because fpsdisplaysink drops one frame every time it displays the counter
# 5. Change "FRAMERATE" below to (result of step 4)/100 (e.g. 2502/100 if 2502 frames were dropped)
FRAMERATE="${FRAMERATE:-2500/100}"
#
# VARIABLES YOU MIGHT NEED TO EDIT
# These are defined in the script, but you can override them here if you need non-default values:
#
# set this to 1 to get lots of debugging data (including DOT graphs of your pipelines):
#DEBUG_MODE=
# Set these to alter the recording quality:
#GST_MPEG4_OPTS="..."
#GST_MPEG4_OPTS_PASS1="..."
#GST_MPEG4_OPTS_PASS2="..."
#GST_LAME_OPTS="..."
# Set these to control the audio/video pipelines:
#GST_QUEUE="..."
#GST_VIDEO_SRC="..."
#GST_AUDIO_SRC="..."
'
#
# CONFIGURATION SECTION
#
CONFIG_SCRIPT="$HOME/.gstreamer-record-scriptrc"
[ -e "$CONFIG_SCRIPT" ] && source "$CONFIG_SCRIPT"
source <( echo "$CONFIGURATION" )
# set this to 1 to get lots of debugging data (including DOT graphs of your pipelines):
DEBUG_MODE="${DEBUG_MODE:-}"
# `gst-inspect` has more information here too:
GST_MPEG4_OPTS="${GST_MPEG4_OPTS:-interlaced=true bitrate=$(( VIDEO_KBITRATE * 1000 )) max-key-interval=15}"
GST_MPEG4_OPTS_PASS1="${GST_MPEG4_OPTS_PASS1:-rc-buffer-size=$(( VIDEO_KBITRATE * 4000 )) rc-max-rate=$(( VIDEO_KBITRATE * 2000 )) rc-min-rate=$(( VIDEO_KBITRATE * 875 )) pass=pass1 $GST_MPEG4_OPTS}" # pictures of white noise will max out your bitrate - setting min/max bitrates ensures the video after a period of snow will be reasonable quality
GST_MPEG4_OPTS_PASS2="${GST_MPEG4_OPTS_PASS2:-pass=pass2 $GST_MPEG4_OPTS}" # pictures of white noise will max out your bitrate - setting min/max bitrates ensures the video after a period of snow will be reasonable quality
GST_LAME_OPTS="${GST_LAME_OPTS:-quality=0}"
# `gst-inspect-0.10 <element> | less -i` for a list of properties (e.g. `gst-inspect-0.10 v4l2src | less -i`):
GST_QUEUE="${GST_QUEUE:-queue max-size-buffers=0 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0}"
GST_VIDEO_FORMAT="${GST_VIDEO_FORMAT:-video/x-raw-yuv,width=$(( ASPECT_W * SIZE_MULTIPLIER )),height=$(( ASPECT_H * SIZE_MULTIPLIER )),framerate=$FRAMERATE,interlaced=true,aspect-ratio=$ASPECT_W/$ASPECT_H}"
GST_AUDIO_FORMAT="${GST_AUDIO_FORMAT:-audio/x-raw-int,channels=2,rate=$AUDIO_BITRATE,depth=16}"
GST_VIDEO_SRC="${GST_VIDEO_SRC:-v4l2src device=$VIDEO_DEVICE do-timestamp=true norm=$NORM ! $GST_QUEUE ! videorate silent=false ! $GST_VIDEO_FORMAT}"
GST_AUDIO_SRC="${GST_AUDIO_SRC:-alsasrc device=$AUDIO_DEVICE do-timestamp=true ! $GST_QUEUE ! audioconvert ! audiorate silent=false ! $GST_AUDIO_FORMAT}"
#
# MAIN LOOP
# You should only need to edit this if you're making significant changes to the way the script works
#
echo_bold() {
echo -e "\e[1m$@\e[0m"
}
show_progress() {
START_TIME="$( date +%s )"
PROGRESS_NEWLINE=
while read HEAD TAIL
do
if [ "$HEAD" = "progressreport0" ]
then
NOW_TIME="$( date +%s )"
echo "$TAIL" | {
read TIME PROCESSED SLASH TOTAL REPLY
if [ "$PROCESSED" -eq 0 ]
then
echo -n $'\r'"$TAIL"
else
echo -n $'\r'"$TAIL ETA:" $( date -d "$(( ( $(date +%s) - $START_TIME ) * ( $TOTAL - $PROCESSED ) / $PROCESSED )) seconds" )
fi
}
PROGRESS_NEWLINE=$'\n'
else
echo "$PROGRESS_NEWLINE$HEAD $TAIL"
PROGRESS_NEWLINE=
fi
done
}
set_directory() {
if [ -z "$1" ]
then
echo "$HELP_MESSAGE"
exit 1
else
DIRECTORY="$( readlink -f "$1" )"
FILE="$DIRECTORY/gstreamer-recording"
URI="file://$( echo "$FILE" | sed -e 's/ /%20/g' )"
mkdir -p -- "$DIRECTORY" || exit
GST_CMD="gst-launch-0.10"
if [ -n "$DEBUG_MODE" ]
then
export GST_DEBUG_DUMP_DOT_DIR="$DIRECTORY/graphs"
if [ -d "$GST_DEBUG_DUMP_DOT_DIR" ]
then
rm -f "$GST_DEBUG_DUMP_DOT_DIR"/*.dot
else
mkdir "$GST_DEBUG_DUMP_DOT_DIR"
fi
GST_CMD="$GST_CMD -v --gst-debug=2"
fi
fi
}
case "$1" in
-i|--i|--in|--ini|--init)
if [ -e "$CONFIG_SCRIPT" ]
then
echo "Please delete $CONFIG_SCRIPT if you want to recreate it"
else
echo "$CONFIGURATION" > "$CONFIG_SCRIPT"
echo "Please edit $CONFIG_SCRIPT to match your system"
fi
;;
-r|--r|--re|--rec|--reco|--recor|--record)
# Build a pipeline with sources being encoded as MPEG4 video and FLAC audio, then being muxed into a Matroska container.
# FLAC and Matroska are used during encoding to ensure we don't lose much data between passes
set_directory "$2"
if [ -e "$FILE-temp.mkv" ]
then
echo "Please delete the old $FILE-temp.mkv before making a new recording"
exit 1
fi
v4l2-ctl --device="$VIDEO_DEVICE" --set-input $VIDEO_INPUT
echo_bold "Press ctrl+c to finish recording"
sudo nice -20 sh -c "echo \$\$ > '$FILE-temp.pid' && exec $GST_CMD -e \
$GST_VIDEO_SRC ! ffenc_mpeg4 $GST_MPEG4_OPTS_PASS1 'multipass-cache-file=$FILE-temp.log' ! $GST_QUEUE ! mux. \
$GST_AUDIO_SRC ! flacenc ! $GST_QUEUE ! mux. \
matroskamux name=mux ! filesink location='$FILE-temp.mkv'"
echo_bold extracting audio...
$GST_CMD -q \
uridecodebin uri="$URI-temp.mkv" \
! progressreport \
! audioconvert \
! audiorate \
! wavenc \
! filesink location="$FILE-temp.wav" \
| show_progress
echo
cat <<EOF > "$FILE.conf"
#
# NOISE REDUCTION (optional)
#
# To reduce noise in the final stream, identify a period in the recording
# which only has background noise (a second or two should be enough)
#
# If you want to reduce noise, set these two variables to the start and
# duration of the noise period (in seconds):
#
NOISE_START=
NOISE_DURATION=
#
# AUDIO DELAY
#
# To add a period of silence at the beginning of the video, watch the .mkv
# file and decide how much silence you want.
#
# If you want to add a delay, set this variable to the duration in seconds
# (can be fractional):
#
AUDIO_DELAY=$AUDIO_DELAY
# Uncomment the following when you've finished editing
# (it's just here to prevent silly mistakes)
# Then re-run the script with --process
#CONFIG_FILE_DONE=done
EOF
cat <<EOF
Now please check $FILE-temp.mkv
If you've recorded the wrong thing, delete it and start again
Otherwise edit $FILE.conf and set any variables you want
EOF
;;
-k|--k|--ki|--kil|--kill)
set_directory "$2"
sudo sh -c "sleep '$3' && kill -s 2 '$(< "$FILE-temp.pid" )'"
;;
-p|--p|--pr|--pro|--proc|--proce|--proces|--process)
set_directory "$2"
[ -e "$FILE.conf" ] && source "$FILE.conf"
if [ -z "$CONFIG_FILE_DONE" ]
then
echo "Please edit $FILE.conf before processing the file"
exit 1
fi
if [ -e "$FILE.avi" ]
then
echo "Please delete the old $FILE.avi before making a new recording"
exit 1
fi
# Add $AUDIO_DELAY seconds of silence to the audio, calculate a noise profile, and reduce noise based on that profile
if [ -n "$NOISE_START$AUDIO_DELAY" ]
then
if [ -n "$NOISE_START" ]
then
exec 6< <( sox -V1 "$FILE-temp.wav" -t wav - trim "$NOISE_START" "$NOISE_DURATION" | sox -t wav - -n noiseprof - )
NOISE_CMD="noisered /dev/fd/6 0.21"
else
NOISE_CMD=
fi
case "${AUDIO_DELAY:0:1}X" in
X)
# NO AUDIO DELAY
exec 3< <( sox -V1 "$FILE-temp.wav" -t wav - $NOISE_CMD )
;;
-)
# NEGATIVE AUDIO DELAY - APPEND SILENCE
exec 4< <( sox -V1 "$FILE-temp.wav" -t wav - trim 0.0 "$AUDIO_DELAY" )
exec 5< <( sox -V1 -n -r "$AUDIO_BITRATE" -c 2 -t wav - trim 0.0 "${AUDIO_DELAY:1}" )
exec 3< <( sox -V1 -t wav /dev/fd/4 -t wav /dev/fd/5 $NOISE_CMD )
;;
*)
# POSITIVE AUDIO DELAY - PREPEND SILENCE
exec 4< <( sox -V1 -n -r "$AUDIO_BITRATE" -c 2 -t wav - trim 0.0 "$AUDIO_DELAY" )
exec 5< <( sox -V1 "$FILE-temp.wav" -t wav - trim 0.0 -"$AUDIO_DELAY" )
exec 3< <( sox -V1 -t wav /dev/fd/4 -t wav /dev/fd/5 $NOISE_CMD )
;;
esac
else
exec 3< "$FILE-temp.wav"
fi
# Do a second pass over the video (shrinking the file size), and replace the audio with the improved version:
echo_bold "building final file..."
nice -n +20 $GST_CMD -q \
uridecodebin uri="$URI-temp.mkv" ! progressreport ! ffenc_mpeg4 $GST_MPEG4_OPTS_PASS2 "multipass-cache-file=$FILE-temp.log" ! $GST_QUEUE ! mux.video_0 \
fdsrc fd=3 ! decodebin ! audioconvert ! audiorate ! lamemp3enc $GST_LAME_OPTS ! $GST_QUEUE ! mux.audio_0 \
avimux name=mux ! filesink location="$FILE.avi" \
| show_progress
echo_bold "Saved to $FILE.avi"
;;
-c|--c|--cl|--clea|--clean)
rm -f "$2"-temp.*
;;
*)
echo "$HELP_MESSAGE"
esac
This script generates a video in two passes: first it records and builds statistics, then lets you analyse the output, then builds an optimised final version.
Bash script to record video tapes with entrans
#!/bin/bash
targetdirectory="~/videos"
# Test ob doppelt geöffnet
if [[ -e "~/.lock_shutdown.digitalisieren" ]]; then
echo ""
echo ""
echo "Capturing already running. It is impossible to capture to tapes simultaneously. Hit a key to abort."
read -n 1
exit
fi
# trap keyboard interrupt (control-c)
trap control_c 0 SIGHUP SIGINT SIGQUIT SIGABRT SIGKILL SIGALRM SIGSEGV SIGTERM
control_c()
# run if user hits control-c
{
cleanup
exit $?
}
cleanup()
{
rm ~/.lock_shutdown.digitalisieren
return $?
}
touch "~/.lock_shutdown.digitalisieren"
echo ""
echo ""
echo "Please enter the length of the tape in minutes and press ENTER. (Press Ctrl+C to abort.)"
echo ""
while read -e laenge; do
if [[ $laenge == [0-9]* ]]; then
break 2
else
echo ""
echo ""
echo "That's not a number."
echo "Please enter the length of the tape in minutes and press ENTER. (Press Ctrl+C to abort.)"
echo ""
fi
done
let laenge=laenge+10 # Sicherheitsaufschlag, falls Band doch länger
let laenge=laenge*60
echo ""
echo ""
echo "Please type in the description of the tape."
echo "Don't forget to rewind the tape?"
echo "Hit ENTER to start capturing. Press Ctrl+C to abort."
echo ""
read -e name;
name=${name//\//_}
name=${name//\"/_}
name=${name//:/_}
# Falls Name schon vorhanden
if [[ -e "$targetdirectory/$name.mpg" ]]; then
nummer=0
while [[ -e "$targetdirectory/$name.$nummer.mpg" ]]; do
let nummer=nummer+1
done
name=$name.$nummer
fi
# Audioeinstellungen setzen: unmuten, Regler
amixer -D pulse cset name='Capture Switch' 1 >& /dev/null # Aufnahme-Kanal einschalten
amixer -D pulse cset name='Capture Volume' 20724 >& /dev/null # Aufnahme-Pegel einstellen
# Videoinput auswählen und Karte einstellen
v4l2-ctl --set-input 3 >& /dev/null
v4l2-ctl -c saturation=80 >& /dev/null
v4l2-ctl -c brightness=130 >& /dev/null
let ende=$(date +%s)+laenge
echo ""
echo "Working"
echo "Capturing will be finished at "$(date -d @$ende +%H.%M)"."
echo ""
echo "Press Ctrl+C to finish capturing now."
nice -n -10 entrans -s cut-time -c 0-$laenge -m --dam -- --raw \
v4l2src queue-size=16 do-timestamp=true device=$VIDEO_DEVICE norm=PAL-BG num-buffers=-1 ! stamp sync-margin=2 sync-interval=5 silent=false progress=0 ! \
queue leaky=2 max-size-buffers=0 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0 ! dam ! \
cogcolorspace ! videorate ! \
'video/x-raw-yuv,width=720,height=576,framerate=25/1,interlaced=true,aspect-ratio=4/3' ! \
queue leaky=2 max-size-buffers=0 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0 ! \
ffenc_mpeg2video rc-buffer-size=1500000 rc-max-rate=7000000 rc-min-rate=3500000 bitrate=4000000 max-key-interval=15 pass=pass1 ! \
queue leaky=2 max-size-buffers=0 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0 ! mux. \
pulsesrc buffer-time=2000000 do-timestamp=true ! \
queue leaky=2 max-size-buffers=0 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0 ! dam ! \
audioconvert ! audiorate ! \
audio/x-raw-int,rate=48000,channels=2,depth=16 ! \
queue max-size-buffers=0 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0 ! \
ffenc_mp2 bitrate=192000 ! \
queue leaky=2 max-size-buffers=0 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0 ! mux. \
ffmux_mpeg name=mux ! filesink location=\"$targetdirectory/$name.mpg\" >& /dev/null
echo "Finished Capturing"
rm ~/.lock_shutdown.digitalisieren
The script uses a command line similar to this to produce a DVD compliant MPEG2 file.
- The script aborts if another instance is already running.
- If not it asks for the length of the tape and its description
- It records to description.mpg or if this file already exists to description.0.mpg and so on for the given time plus 10 minutes. The target-directory has to be specified in the beginning of the script.
- As setting of the inputs and settings of the capture device is only partly possible via GStreamer other tools are used.
- Adjust the settings to match your input sources, the recording volume, capturing saturation and so on.
Further documentation resources
- Gstreamer project
- FAQ
- Documentation
- man gst-launch
- entrans command line tool documentation
- gst-inspect plugin-name